Genel Bilgiler
Book your appointment
Reserve your free consultation with our health team in minutes.
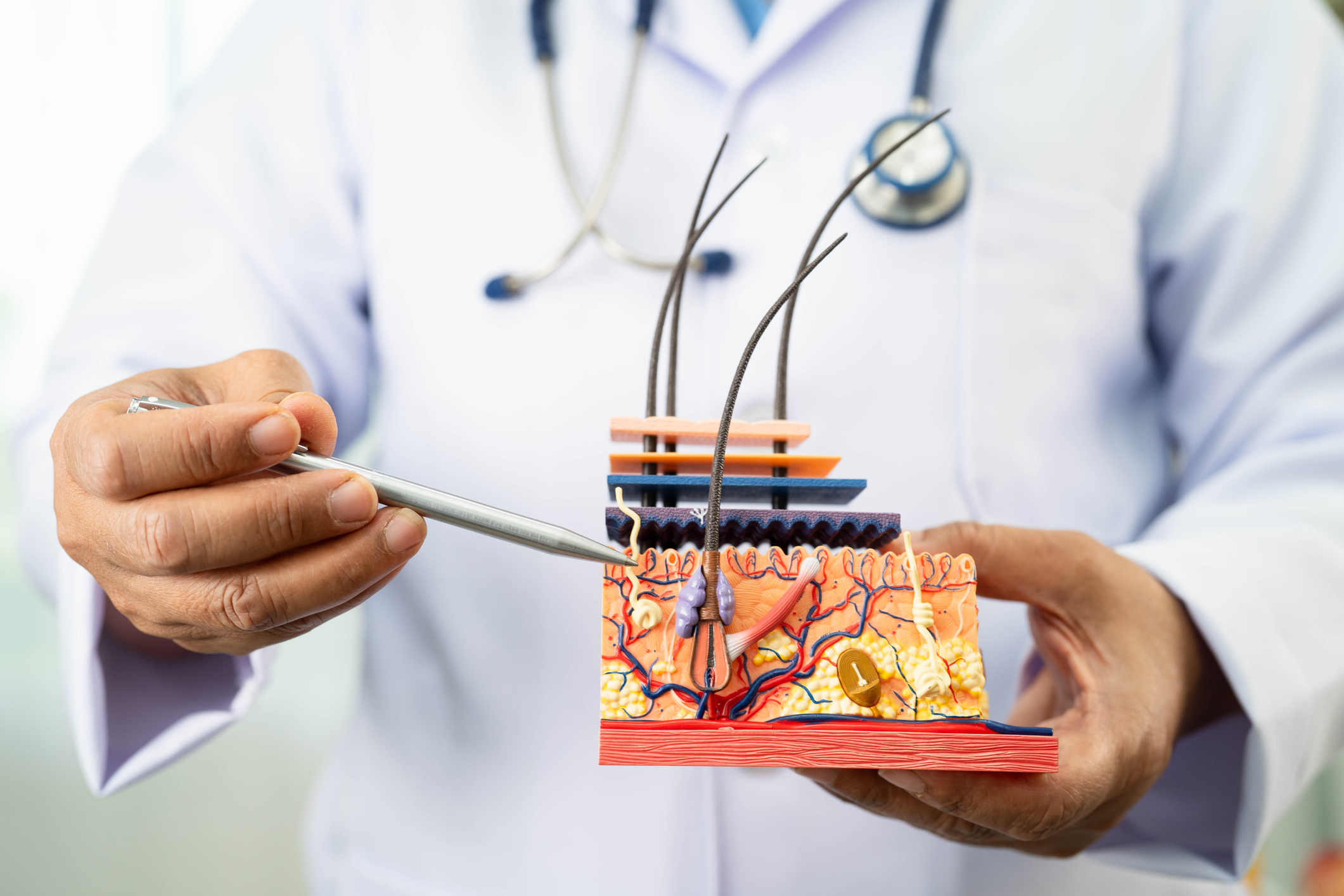
You can find basic information about the hair transplant process, methods used, recovery period, and important precautions on this page. We share the most up-to-date and accurate details to help you make a healthy and informed decision.
General Information
Male Pattern (Androgenetic) Hair Loss and Hair Transplantation
Our hair follicles, which produce hair strands, usually work for several years before entering a resting phase. During this resting phase, the connection between the hair strand and its root loosens, causing the hair to shed with washing, combing, or brushing. After shedding, the resting follicle begins to produce a new hair strand within 2-4 months. This cycle of shedding and regrowth happens at different times for each follicle. While some hairs fall out daily, new hairs start to grow in others. On average, about 50-100 hairs fall out and regrow each day. When the balance between hair loss and new growth is disrupted, baldness begins to appear. This usually indicates that roughly half of the hair in terms of number and thickness has been lost. The greater the proportion of lost hair compared to new growth, the more advanced the baldness becomes.


Male Pattern (Androgenetic) Hair Loss and Hair Transplantation
Male pattern hair loss is the most common type of hair loss in humans, including women. It’s also known as androgenetic or genetic hair loss. The exact timing and severity of this hair loss can’t be predicted, but genetic predisposition is key. The genes inherited from your parents determine before birth whether your hair will thin or fall out later in life. Those with a family history of noticeable hair loss often start losing hair in their twenties. Hair loss most commonly appears between ages 25 and 35 and typically slows down after age 45.
The main hormone responsible for androgenetic hair loss is Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), present in both men and, in smaller amounts, women. Hair follicles prone to shedding contain high levels of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. DHT negatively affects these follicles, causing hair thinning, weakening, and eventually hair loss. Hair on the back of the head and sides doesn’t contain this enzyme and usually doesn’t fall out, which is why these areas are used as donor sites in hair transplant procedures.
Male Pattern (Androgenetic) Hair Loss and Hair Transplantation
Many treatment methods have been tried for male pattern hair loss. Despite extensive research over the last 20 years, only two active ingredients have been proven effective and approved by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration).
However, these medications do not work for everyone, require continuous use, may cause side effects, and involve significant long-term costs, which limits their overall success in curing baldness. Besides medications, other treatments like low-level laser therapy, mesotherapy, and PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) are also used, but none have yet been proven effective or officially approved.
Today, hair transplantation is considered the safest and most effective method to restore lost hair in both men and women with genetic hair loss. Success in hair transplantation is also limited if the patient does not have a sufficient number of healthy donor hair follicles. In such cases, a careful distribution of grafts is essential—for example, placing a denser concentration of grafts in the front hairline and fewer in the back to optimize results.
Book an appointment
Take the first step toward natural hair today.

General Information
Hair Transplantation for Hair Loss Due to Injuries
Hair transplantation is successfully used to cover bald areas in the hair, eyebrows, mustache, and beard caused by accidents, previous surgeries, and burns. Especially with the micro FUE and DHI methods, hair loss is covered with a natural appearance.
General Information
Failed Hair Transplant
Redo Hair Transplant
The best solution for a failed hair transplant is a new hair transplant. It is a reasonable choice to have a new transplant to cover sparse areas and unnatural-looking hair left from the unsuccessful transplant. With advancements in hair transplantation, poorly performed hair transplants from previous years can be corrected using the mFUE + DHI method.
Hair transplantation for densification can also be done for those who have had a previous transplant and are not satisfied with their hair density. The only requirement for this is having enough hair follicles remaining in the donor area at the nape and sides of the head.
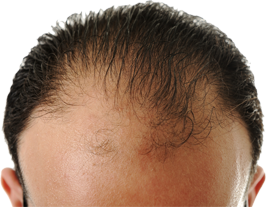
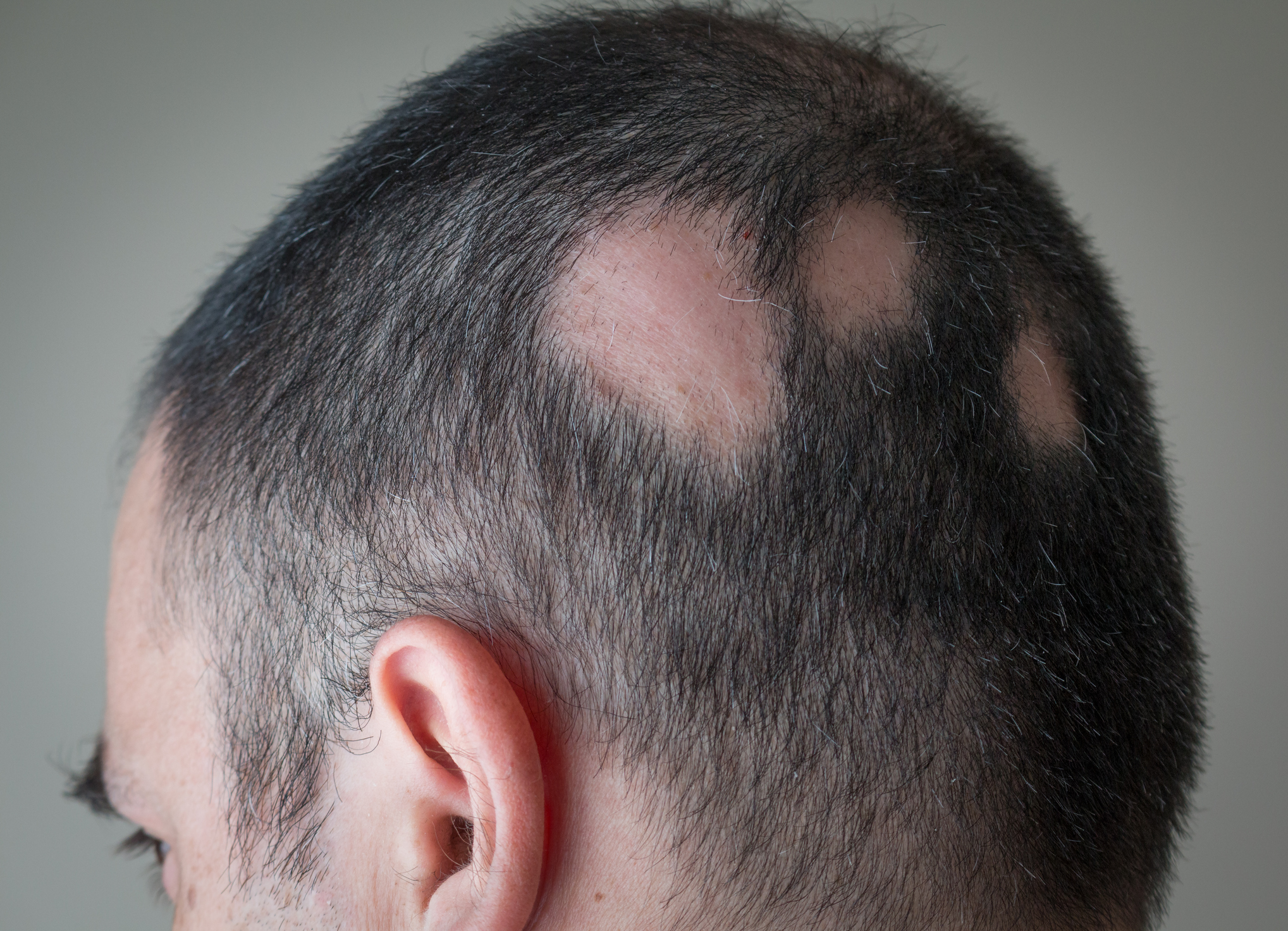
General Information
Hair Transplant
After Certain Diseases
Severe physical or mental stress, certain medications, anemia, Trichotillomania (pathological, compulsive hair pulling disorder), some hormonal diseases, diabetes, infections, or conditions such as Alopecia areata, psoriasis, and eczema can cause hair loss. In these cases, the primary treatment is to address the underlying cause or disease responsible for the hair loss. Hair transplantation can be performed on patients with a suitable donor area when hair does not regrow in the long term or when regrowth is unlikely.
Frequently Asked Questions
Men with genetically caused hair loss,
Women experiencing male-pattern hair loss,
Individuals with scars, hair, beard, mustache, or eyebrow loss due to accidents, surgeries, burns, or similar reasons,
People who have had unsuccessful hair transplants before,
Those who have had hair transplants but are not satisfied with hair density,
Patients whose hair loss is caused by certain diseases and whose hair does not regrow in the long term despite treatment, provided there are suitable donor areas available,
Hair transplantation can be performed.
There is no strict age limit for hair transplantation. It is generally performed on individuals between the ages of 20 and 65.
A graft is a piece of tissue taken from one part of the body and transplanted to another for repair. In hair transplantation, "graft" refers to a tissue containing hair follicles.
Hair follicles that make up our hair usually come in groups containing 1-5 hair roots. These groups of hair follicles are called "follicular units."
Grafts containing hair follicles are taken from the back and sides of the head using micro motor punch needles sized 0.60-0.80 mm, each containing part of a follicular unit. In the classic method, the extracted grafts are placed into channels made with sharp tools in the bald area. In the DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) method, the implanter pen creates the channel and implants the graft simultaneously.
Absolutely not. While FUE was once performed manually, today it is almost standard to use micromotors. Some supporters of the manual FUE method previously claimed otherwise. However, studies have found no difference between manual and micromotor graft extraction.
The duration depends on the number of grafts to be transplanted.
2,000-3,000 grafts (about 4,500-7,000 hairs) take 5-6 hours.
4,000-5,000 grafts (about 9,000-11,000 hairs) take 7-8 hours.
Yes, it is possible for suitable candidates. Transplantation can be done in areas with long hair while keeping the donor area concealed.
Most transplanted hairs shed or weaken in the first few months. This happens because some hair follicles enter a resting phase to heal after the transplant. After 2-4 months, the shed hairs start to grow back. Nearly all transplanted hairs emerge within 8 months. Initially curly and thin hairs gradually straighten and thicken by the 10th month, and this thickening continues up to one year after the transplant.
This is a normal condition. It happens because buried follicles try to break through the skin. During this process, first consult your doctor and follow cleaning guidelines; you can gently pop the swelling's tip with a clean needle.
Hair follicles from the back and sides of the head are genetically resistant to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and do not fall out for life. Since grafts in the Micro FUE + DHI method are taken from these areas, the transplanted hairs do not fall out permanently.
When medical protocols are followed, there are no known side effects or health risks associated with hair transplantation using the Micro FUE + DHI method.
Currently, hair transplantation is the most effective treatment for restoring lost hair for various reasons. Although research on hair cloning is ongoing, no concrete results have been achieved yet.
If a second transplant is planned to increase density in the same area, you should wait 8 months to see the full growth of the first transplant. For transplanting to a different area, waiting 3-4 months for the donor area to heal is advisable. Hair follicles can be taken from the same area for a second or even third transplant. However, the donor area will gradually thin out. Careful attention is needed to avoid scars and thinning.
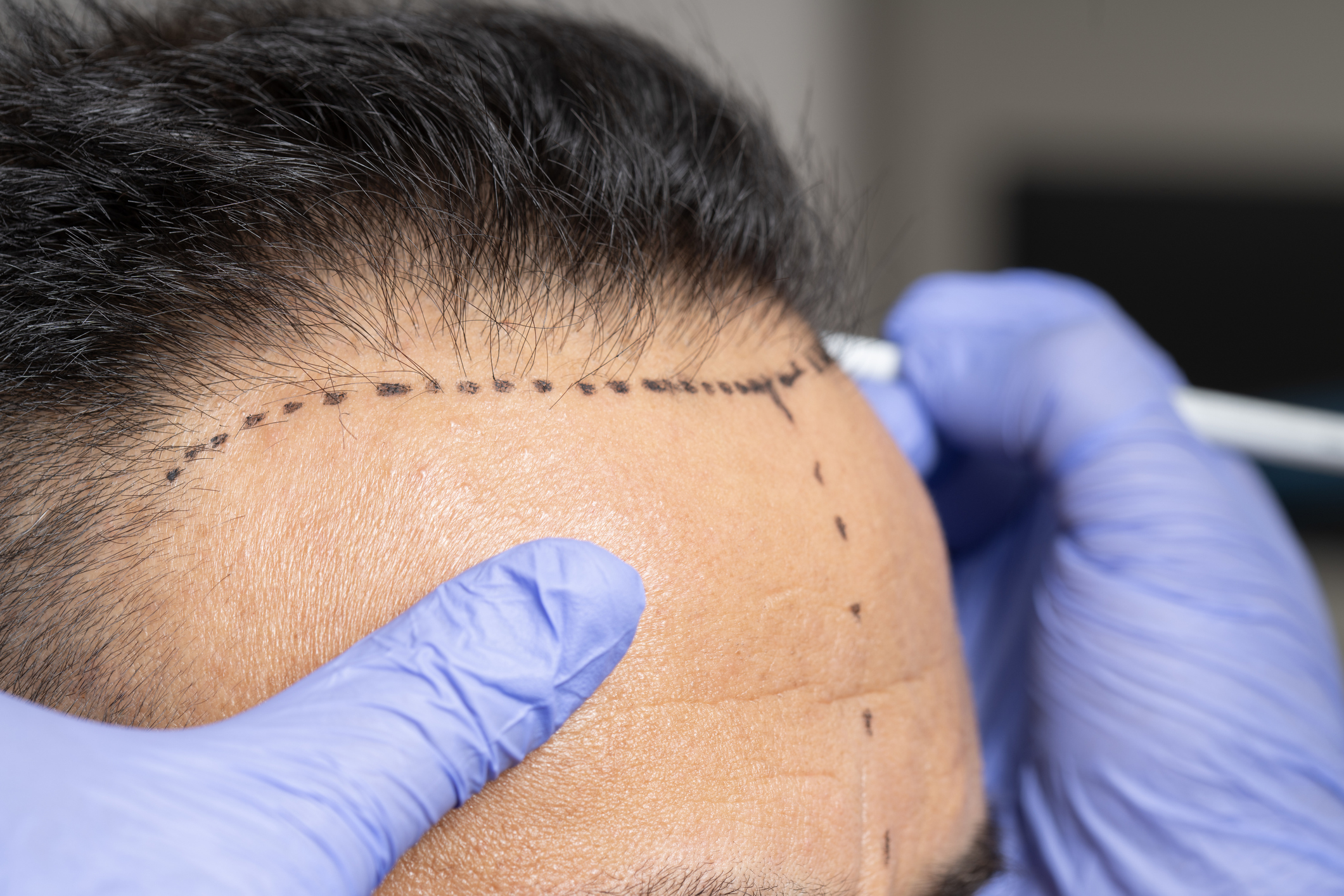
FUE and DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) methods
FUE and DHI methods are modern hair transplantation techniques that complement each other in terms of follicle extraction and implantation, offering natural results and fast recovery.

Things to Consider Before Hair Transplantation
Before a hair transplant, it is important to eat healthily, quit smoking and alcohol, inform your doctor about any medications, and follow the doctor’s recommended preparations.
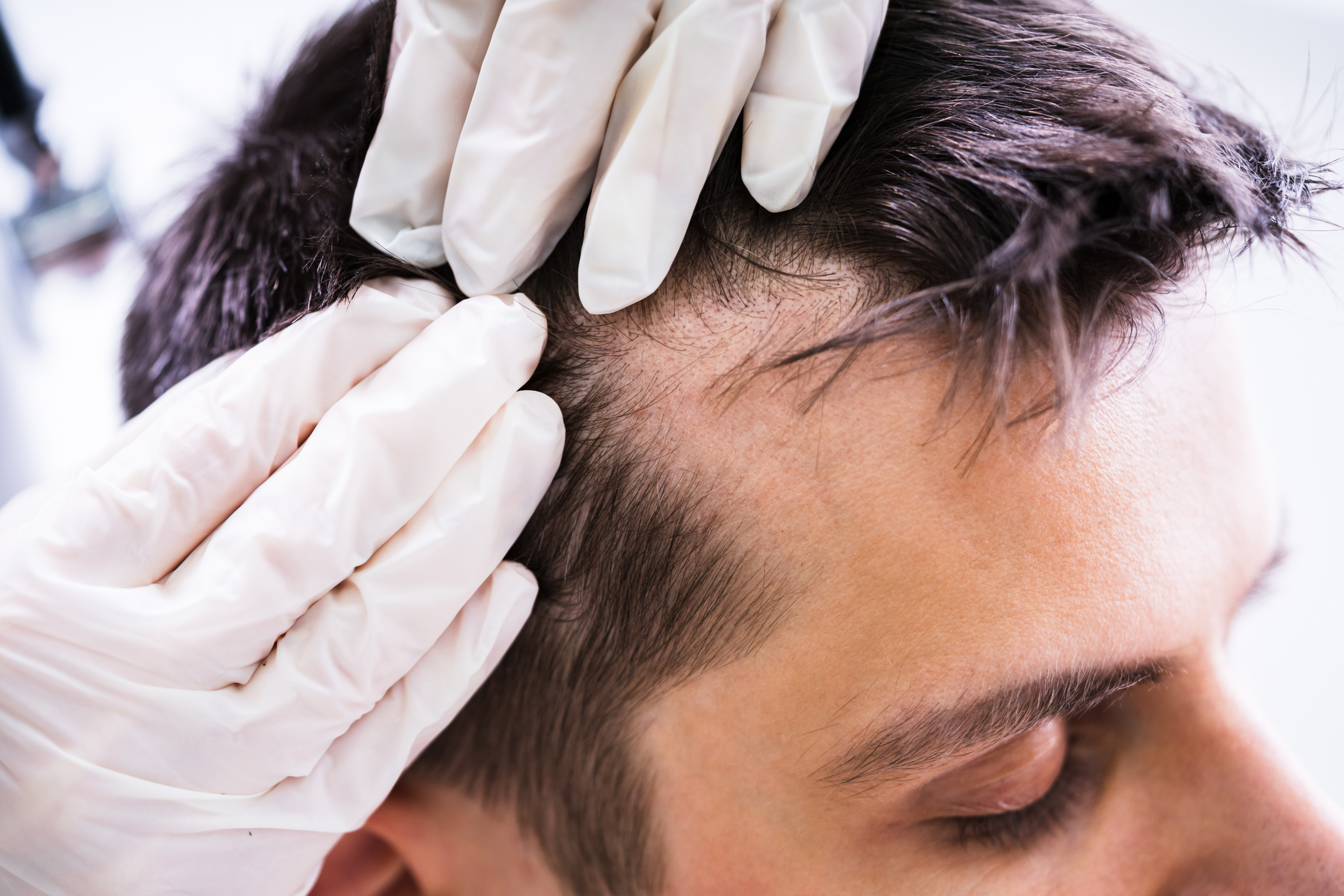
Things to Consider After Hair Transplantation
After a hair transplant, it is important to be careful during recovery, follow the given instructions, and protect the treated area.

